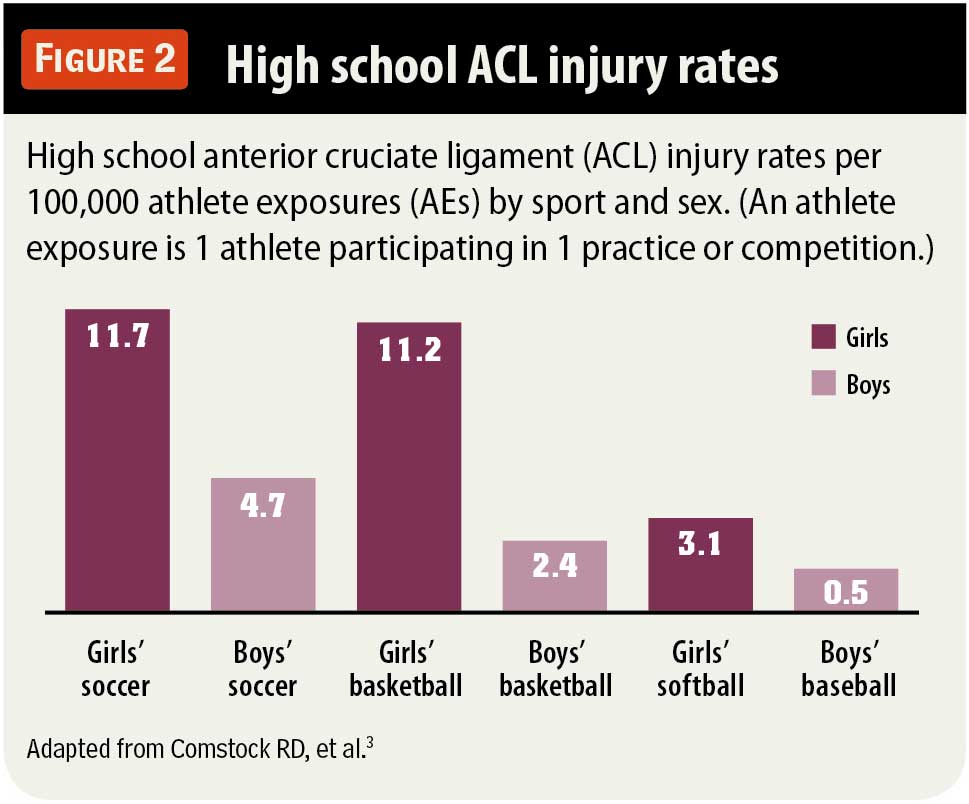
ACL injury rates in women athletes have become a significant concern in the sports community, particularly as female participation in competitive sports increases. Studies indicate that women are at a 1.7 times higher risk of sustaining an ACL tear compared to their male counterparts, raising questions about the underlying causes. Factors contributing to these elevated rates include not only biological differences but also social dynamics, including training resources and team sizes. Researchers emphasize that addressing these gender differences in sports injuries requires a comprehensive approach to female athlete injury prevention. By understanding the complexities behind women’s sports injury rates, we can work towards creating safer athletic environments for women athletes.
The topic of ACL injuries among female competitors highlights critical issues related to gender disparities in sports. Female athletes experience a notably higher incidence of anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries, prompting a closer examination of the causes and consequences. This phenomenon is linked to various factors, ranging from anatomical differences to the socio-economic aspects affecting women in sports. In exploring the reasons behind these injuries, it becomes essential to consider the specific circumstances surrounding women athletes, including their training regimens and the support systems in place for them. Comprehensive analyses and improved methodologies in injury assessment are crucial for advancing female athlete health and safety.
Understanding ACL Injury Rates in Women Athletes
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is a crucial stabilizing structure in the knee that is susceptible to injury, particularly among women athletes. Research shows that women sustain ACL injuries at a rate 1.7 times higher than their male counterparts, which has led to extensive investigations into the underlying causes of this discrepancy. Factors such as hormonal differences, hip structure, and body mechanics have often been cited as biological reasons for this increased risk, leading to common misconceptions about why these injuries are prevalent in female sports. However, recent studies advocate that the issue is more complex and influenced significantly by social factors.
The recent study published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine highlights that the reasons behind the higher rates of ACL injuries in women athletes extend beyond biological differences. It emphasizes that the allocation of resources in sports often favors men’s teams, which results in women competing in smaller, less equipped squads. This skew in resources directly influences training intensity, competition frequency, and ultimately, injury risk. By shifting the narrative from a purely biological explanation to one that includes social equity in sports, we can better understand the multifaceted nature of these injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main reasons for higher ACL injury rates in women athletes?
The higher ACL injury rates in women athletes can be attributed to a combination of biological and social factors. While previous studies pointed to hormonal differences and anatomical variations, a recent study emphasizes that social conditions, such as underfunding and smaller team sizes, play a significant role. Women athletes often have less training time compared to their male counterparts, contributing to higher injury risks.
How do ACL tear causes differ between male and female athletes?
ACL tear causes in female athletes often relate to a complex interplay of anatomical, hormonal, and social factors. Females may experience increased injury rates due to differences in muscle strength, joint laxity, and training conditions that do not fully prepare them for competitive play. Overlooked training and preparation disparities, along with fewer resources, further elevate these risks.
What is the impact of sports injury rates on women’s sports?
Sports injury rates among women athletes, particularly ACL injuries, highlight significant disparities in training, funding, and support compared to men’s sports. Higher injury rates can lead to reduced participation and diminished performance, raising concerns about the long-term viability and growth of women’s sports.
Are there gender differences in sports injuries beyond ACL injuries?
Yes, research indicates gender differences in various sports injuries beyond ACL injuries. Female athletes are often found to be more susceptible to specific injuries due to anatomical and physiological differences, as well as variations in training approaches and exposure to competition. These factors suggest that injury prevention strategies should be tailored to account for these differences.
What measures can be taken for female athlete injury prevention in ACL injuries?
Injury prevention for female athletes, particularly concerning ACL injuries, can be improved by implementing targeted training programs that emphasize strength, conditioning, and biomechanics. Additionally, addressing social disparities in access to quality coaching and resources, as well as creating equitable training opportunities, could significantly reduce female athlete injury rates.
How do athlete-exposure metrics affect ACL injury rate assessments in women athletes?
Athlete-exposure metrics, traditionally used to assess ACL injury rates, often do not accurately reflect the reality of women’s sports. Many studies have simplified these metrics without accounting for the differences in competition time, practice frequency, and team size, which can lead to underestimating the risks female athletes face. A more nuanced approach to measuring these exposures is essential for accurate assessments.
How does training time correlate with ACL injury risks in women athletes?
Training time is a crucial factor in ACL injury risks for women athletes. Research shows that injuries are more likely to occur during games, and if female athletes train less than their male counterparts due to smaller team sizes or lower investment in women’s sports, this discrepancy can heighten their risk of ACL injuries. Enhancing training time and conditioning can help mitigate these risks.
What role do social factors play in ACL injury rates for women athletes?
Social factors significantly influence ACL injury rates in women athletes. Inequities in funding, access to quality facilities, and coaching resources create an environment where female athletes may not receive the same level of preparation and training as their male peers, leading to higher rates of injuries like ACL tears. Recognizing and addressing these social disparities is essential for improving overall safety and health in women’s sports.
| Parameter | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Roster size-based AEs | 28 | 25 |
| Participant-based AEs | 19 | 17 |
| Player-hours | 6 | 6 |
| Injury rate per 100 roster-based AEs | 3.6 | 4.0 |
| Injury rate per 100 participant-based AEs | 5.3 | 5.9 |
| Injury rate per 100 player-hours | 16.7 | 16.7 |
| Injury risk per team member | 0.036 | 0.040 |
| Injury risk per participant | 0.053 | 0.059 |
Summary
ACL injury rates in women athletes are notably higher compared to their male counterparts, a discrepancy often attributed to biological factors like hormone cycles and anatomy. However, recent research from Harvard’s GenderSci Lab highlights that social factors, including disparities in team sizes, training conditions, and competition exposure, play a significant role. The study reveals that women athletes experience a higher frequency of ACL injuries not solely due to biology but largely due to systemic inequities in sports. This calls for a reconsideration of current methodologies used in calculating injury rates to ensure they accurately reflect the complexities of gender dynamics in athletics, enabling better prevention strategies.